The basics of PTC
PTC thermistor
PTC is the abbreviation of Positive Temperature Coefficient, meaning positive temperature coefficient, generally refers to a large positive temperature coefficient of semiconductor materials or components. Usually we refer to the PTC is a positive temperature coefficient thermistor, referred to as PTC thermistor. A PTC thermistor is a typical temperature-sensitive semiconductor resistor whose resistance rises steeply as its temperature rises above a certain temperature (Curie temperature).
PTC thermistor structure and function of the organization
Ceramic materials are commonly used as high-resistance insulators, and ceramic PTC thermistors are based on barium titanate doped with other polycrystalline ceramic materials with low resistance and semiconducting properties. This is achieved by purposeful doping with a material of higher valence as a lattice element of the crystal: a portion of the barium or titanate ions in the lattice is replaced by higher valent ions and a certain amount Produce conductive free electrons. The reason for the PTC thermistor effect, that is, an increase in the resistance step, is that the material texture is composed of many small crystallites that form a potential at the grain boundaries (so-called grain boundaries) Barriers prevent electrons from crossing into the adjacent area, resulting in high electrical resistance that is canceled at low temperatures: the high dielectric constant at the grain boundaries and the spontaneous polarization hinder at low temperatures The formation of a potential barrier allows electrons to flow freely. And this effect at high temperature, the dielectric constant and polarization intensity significantly reduced, resulting in a substantial increase in potential barriers and resistance, showing a strong PTC effect.
PTC thermistor manufacturing process
The mixture (barium carbonate and titanium dioxide and other materials) that can meet the electrical performance and thermal performance requirements is weighed, mixed and then wet-ground, dried and dehydrated to be formed into a disk shape, a rectangular shape, a circular ring shape and a honeycomb shape Rough. These pressed blanks sintered at higher temperatures (about 1400 ℃) into a ceramic, then the upper electrode to metalize the surface, according to the resistance of the sub-file detection. Solder the package or assemble the enclosure according to the structure of the finished product before proceeding with the final full inspection.
Weighing >> Ball mill >> Pre-sintering >> Granulation
>> Molding >> Sintering >> Upper electrode >> Resistance sorting
>> Brazing >> Package Assembly >> Marking >> Withstand Voltage Testing
>> Resistance Testing >> Final Testing >> Packaging >> Storage
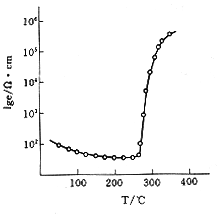
PTC thermistor temperature dependency (R-T characteristics)
Resistance - temperature characteristics commonly referred to as the temperature resistance characteristics, refers to the specified voltage, PTC thermistor zero power resistance and resistor temperature dependence between.
Zero-power resistance, is measured at a temperature PTC thermistor value, plus the PTC thermistor power consumption is very low, low as a result of its power consumption caused by PTC thermistor resistance changes can be ignored Excluding. Rated zero-power resistance refers to the ambient temperature measured at 25 ℃ zero-power resistance.
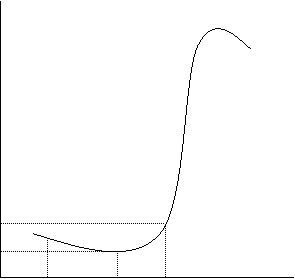
lgR (Ω)
Rmin: minimum resistance
Tmin: Rmin temperature
RTc: 2 times Rmin
Tc: Curie temperature
RTc
Rmin
T25 Tmin Tc T (° C)
An important parameter to characterize the resistance property is the temperature coefficient α, which reflects the steepness of the resistance temperature characteristic curve. The larger the temperature coefficient α, the more sensitive the PTC thermistor is to the temperature change reaction, that is, the more obvious the PTC effect is, the better the corresponding PTC thermistor performance is and the longer the service life is. PTC thermistor temperature coefficient is defined as the temperature changes caused by the relative change in resistance. α = (lgR2-lgR1) / (T2-T1) Under normal circumstances, T1 Tc +15 ℃, T2 Tc +25 ℃ to calculate the temperature coefficient.
The company is located in:
Voltage vs. Current (V-I Characteristics)
Voltage - current characteristics referred to as volt-ampere characteristics, which shows the PTC thermistor in the case of electrical load reaches thermal equilibrium, voltage and current interdependencies.
I(A)
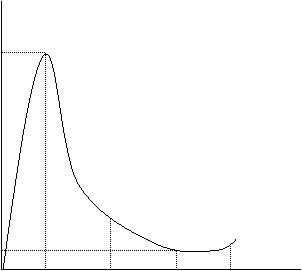
Ik
Ik in the applied voltage Vk when the operating current
Ir Applied voltage Vmax residual current
Vmax maximum operating voltage
VN rated voltage
VD breakdown voltage
Ir
Vk VN Vmax VD V(v)
The volt-ampere characteristics of a PTC thermistor can be roughly divided into three areas:
The region between 0 and Vk is called the linear region. The relationship between voltage and current here basically complies with Ohm's law and does not produce significant nonlinear changes. It is also called non-action region. The region between Vk and Vmax is called the transition region. At this moment, due to the self-heating of the PTC thermistor, the resistance value jumps and the current decreases as the voltage increases. Therefore, this region is also called the operating region. The area above VD is called the breakdown area. At this time, the current increases with the increase of voltage. The resistance of PTC thermistor decreases exponentially. The higher the voltage is, the larger the current is. The PTC thermistor temperature is higher High, but the lower the resistance, quickly lead to thermal breakdown PTC thermistor. The volt-ampere characteristic is an important reference characteristic for over-load protection PTC thermistors.
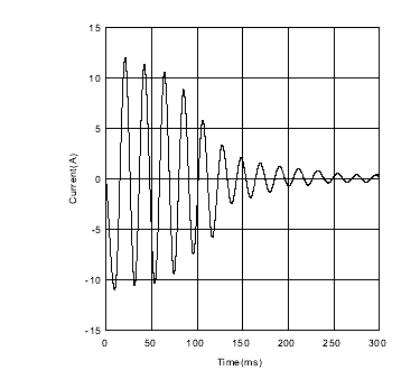
Current vs. time (I-t characteristics)
The current-time characteristic is the characteristic of a PTC thermistor that changes with time during the application of voltage. The beginning of the instantaneous power-on current is called the starting current and the current at the time of thermal equilibrium is called the residual current.
A certain ambient temperature, the PTC thermistor to add an initial current (guaranteed to be the operating current), through the PTC thermistor current is reduced to 50% of the starting current time is the operating time. Current-time characteristics are automatic degaussing PTC thermistor, delay start PTC thermistor, overload protection PTC thermistor important reference characteristics.